EB-1 Extraordinary Ability / Outstanding Researchers or Professors / Multinational Manager or Executives Green Card
 The common process for obtaining an EB-1 green card is composed of two phases: (1) the visa petition and (2) the application for permanent residence. There are three EB-1 green card subcategories. They are:
The common process for obtaining an EB-1 green card is composed of two phases: (1) the visa petition and (2) the application for permanent residence. There are three EB-1 green card subcategories. They are:
The Visa Petition: EB-1A Extraordinary Ability
An EB-1A Extraordinary Ability classification applies to foreign nationals who can demonstrate that they "have risen to the very top of their field of endeavor." Such candidates may apply for EB-1A petition without a labor certification or a job offer (i.e. an employer’s sponsorship). Any foreign national living in the U.S. or abroad may apply if he/she meets the following requirements:
- Foreign national has extraordinary ability in the sciences, arts, education, business or athletics which has been demonstrated by sustained national or international acclaim.
- Foreign national’s achievements have been recognized in the field through extensive documentation.
To establish that the foreign national is a top member within his/her respective field, evidence of receipt of an internationally recognized award such as the Nobel Prize or an Academy Award is accepted. However, in the absence of an internationally recognized award, the foreign national can establish him/herself as a foreign national of Extraordinary Ability by providing documentation of any three (3) of the following:
- Receipt of lesser nationally or internationally recognized prizes or awards for excellence.
- Membership in associations which require outstanding achievements of their members, as judged by recognized national or international experts in their fields.
- Published material in professional/major trade publications or major media about the foreign national and relating to the foreign national's work field.
- Participation as a judge (individually or as a part of a panel) evaluating the work of others.
- Original scientific, scholarly, or artistic contributions of major significance.
- Authorship of scholarly articles in professional journals or other major media.
- Artistic exhibitions/shows.
- Leading role within an organization/establishment with a distinguished reputation.
- High salary/compensation for services in comparison to others.
- Commercial success within the performing arts, as shown by either box office receipt figures or cassette, compact disk, video, or DVD sales figures.
In addition to the above criteria, the foreign national must prove that he/she will continue to pursue work in the area of extraordinary ability in the U.S. Procedurally, the EB-1A is an I-140 Immigration Petition, Petition for Foreign national Worker application. The foreign national may petition for him/herself by filing Form I-140 with supporting documentation that demonstrate that the foreign national meets fundamental EB-1A criteria. The petition is one of the fastest ways to obtain a Green Card.
The Visa Petition: EB-1B Outstanding Researcher or Professor
An EB-1B Outstanding Researcher or Professor classification applies to foreign nationals who are internationally recognized as outstanding in a particular scientific or scholarly field. Unlike self-petitioned EB-1A cases, EB-1B cases are employer sponsored. This means the petitioning employer must demonstrate that the foreign national has outstanding ability as a researcher or professor and has a permanent job offer from the employer. The outstanding researcher/professor foreign national must have the sponsorship of his/her employer throughout the petitioning process. The employer is the petitioner and the outstanding researcher/professor is the beneficiary for the EB-1B process.
There are three (3) main requirements for someone seeking a petition as an "Outstanding Researcher/Professor", including:
- International recognition for being outstanding in a specific academic field;
- At least three years of relevant research or teaching experience: Research or teaching experience obtained while in pursuit of an advanced degree, such as a Ph.D., can be counted toward the three year requirement, but only if the foreign national has acquired the degree, and if the teaching duties were such that he or she had full responsibility for the class taught or if the research conducted toward the degree has been recognized within the academic field as outstanding. The foreign national must document his or her work history with letters from current and/or former employers describing work duties and years of employment; and
- A job offer for a permanent research position or a tenured or tenure-track teaching position from the sponsoring employer: Generally, the job offer is given by a university or other similar academic or scientific institution, but it can also be offered by a private employer. If the offer is from a private employer, the employer must have at least three full-time researchers along with accompanying documentation supporting their accomplishments within the field.
The Visa Petition: EB-1C Multinational Managers or Executives
Certain multinational executives or managers can obtain their green cards by showing that they served for at least one year in another country in an executive or managerial position with the parent, subsidiary, or affiliated company of a U.S. company. This process requires the individual to have a permanent job offer from the U.S. company to work in an executive or managerial position.
To qualify for a green card as a Multinational Manager or Executive, the foreign national must show he/she was employed by a company affiliated with the foreign national current U.S. employer as a manager or executive outside the U.S. for at least one year out of the three years before his/her transfer to the United States.
The Multinational Manager/Executive category for employment-based green cards closely resembles the L-1A visa category. Therefore, many people who qualify for an L-1A visa as a Manager or Executive would also qualify for permanent residency in the United States, without a labor certification application.
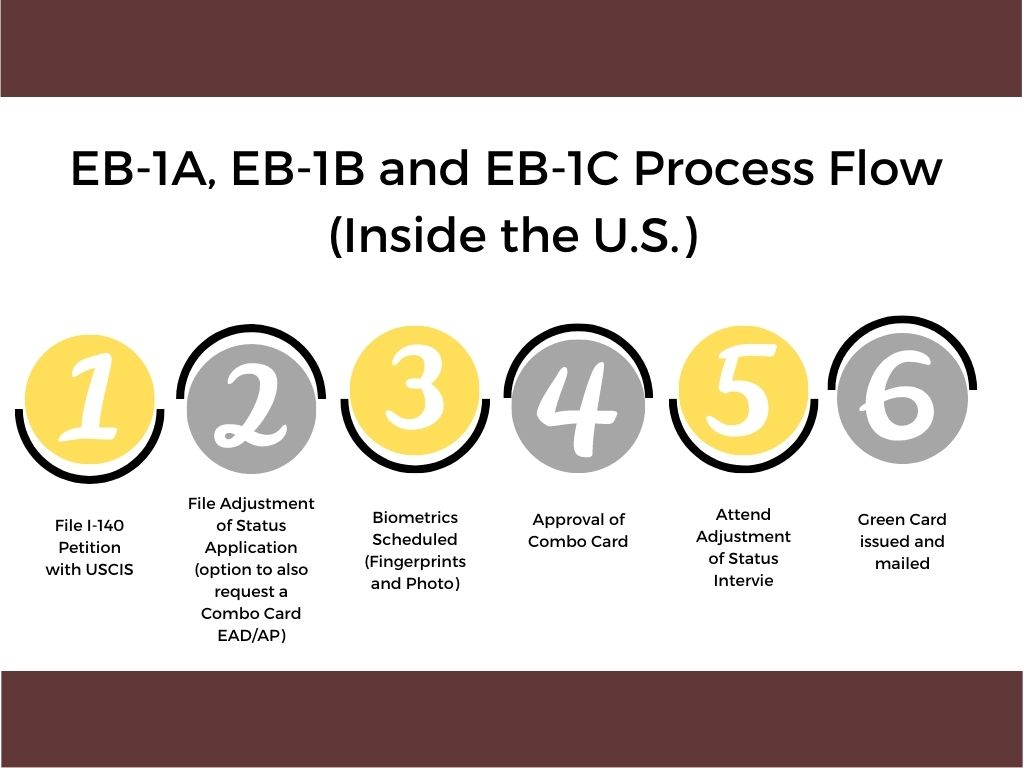
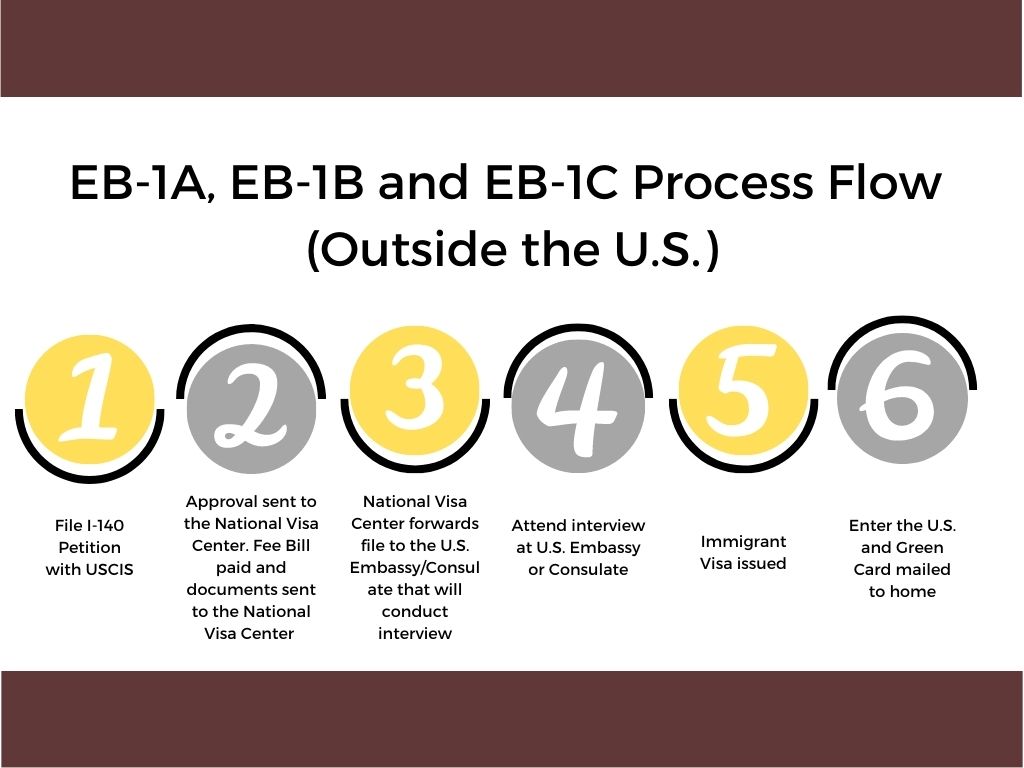
Application for Lawful Permanent Residence
Presuming there is no backlog for an immigrant visa for the foreign national’s country of chargeability and preference category as determined by the filing of the visa petition (i.e., priority date), if the foreign national is in the United States on a temporary nonimmigrant visa, or if he or she otherwise qualifies by regulation, the foreign national and his or her family may be eligible to apply for adjustment of status to lawful permanent resident with the regional service center of USCIS. If the foreign national is not in the United States, or does not qualify for adjustment of status, then the foreign national and his or her family must apply for immigrant visas at the appropriate U.S. consulate in his or her home country or country of residence. If permanent residence is applied for in the United States, it is called “adjustment of status” processing. If applied for outside the United States, it is called applying for an immigrant visa.” The result of either is the same: permanent residence.
As part of the ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application process, a foreign national may also apply for an employment authorization document (EAD) and advance parole (AP). A foreign national is not required to apply for an EAD or AP at the time he/she files his/her ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application or while his/her ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application is pending. It can take U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS, legacy Immigration and Naturalization Service) several months to approve a foreign national’s ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application. If a foreign national’s circumstances change during that time period, having the approved EAD and AP available will provide maximum flexibility even if for now a foreign national plan to continue to maintain his/her nonimmigrant status (such as H-1B, L-1, or O-1 status).
What is an EAD?
A foreign national can obtain an EAD card by filing an EAD Application at the same time he/she files his/her ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application, or after the ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application is filed. Once approved, the EAD card allows its holder to work for any employer while the card is valid. By contrast, a foreign national’s nonimmigrant status (H-1B, O-1, L-1, etc.) allow him/her to work only for the employer who filed the nonimmigrant petition. Once a foreign national has an EAD in hand, he/she may legally work for any employer (but remember that even with an EAD, a foreign national must have the intent to work for the sponsoring employer, in case of employment-based permanent residence, at the time his/her ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application is approved). EADs are valid for up to one year at a time. Spouses and dependent children may also obtain EADs, if desired.
What is an Advance Parole?
A foreign national can obtain AP by filing an AP Application at the same time he/she files his/her ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application, or after the ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application is filed. Once approved, AP allows a foreign national to leave the United States and re-enter without having a valid nonimmigrant visa stamp in his/her passport. Unless a foreign national is maintaining H-1B or L-1 status, after his/her ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application is filed, a foreign national must obtain AP before leaving the United States. For example, if a foreign national has O-1 status and he/she files an ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application and then later a he/she leaves the United States without AP, his/her ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application will be considered by USCIS to have been “abandoned” and will be denied. This would cause great delay and expense because it could take weeks or months to get a foreign national back to the United States in new O-1 status, and then a new ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application package would have to be filed all over again. Traveling with AP prevents such problems from occurring. AP is valid for multiple entries during the validity of the document.
At the lawful permanent residence application stage, the USCIS (or consular office) will ask whether the foreign national has: (1) been a member of the Communist Party, terrorist groups, or similar organizations; (2) been arrested or convicted of any crimes; (3) ever received public assistance, (4) lied to obtain a visa, (5) worked in the United States without permission, or (6) overstayed his/her legal status, etc. We will go into more detail about these factors later.
In general, employment-based and family-based adjustment of status cases are subject to interviews with the local USCIS district office. Individuals who undergo consular processing of employment-based or family-based cases are also required to attend an interview.
At the end of this step, the foreign national will be granted permanent residence and issued a “green card.”