EB-5 Immigrant Investor Green Card
 The EB-5 immigrant visa category allows investors (and their spouses and unmarried children under 21) are eligible to apply for a Green Card (permanent residence) if they:
The EB-5 immigrant visa category allows investors (and their spouses and unmarried children under 21) are eligible to apply for a Green Card (permanent residence) if they:
- Make the necessary investment in a commercial enterprise in the United States; and
- Plan to create or preserve 10 permanent full-time jobs for qualified U.S. workers.
Congress created the EB-5 Program in 1990 to stimulate the U.S. economy through job creation and capital investment by foreign investors. In 1992, Congress created the Immigrant Investor Program, also known as the Regional Center Program, which sets aside EB-5 visas for participants who invest in commercial enterprises associated with regional centers approved by USCIS based on proposals for promoting economic growth.
The common process for obtaining an EB-5 green card is composed of two phases: (1) the visa petition and (2) the application for permanent residence.
The Visa Petition
The purpose of the visa petition is to prove to USCIS that the foreign national qualifies as an investor.
All EB-5 investors must invest in a new commercial enterprise that was established:
- After Nov. 29, 1990; or
- On or before Nov. 29, 1990, that was:
- Purchased and the existing business is restructured or reorganized in such a way that a new commercial enterprise results; or
- Expanded through the investment, resulting in at least a 40% increase in the net worth or number of employees.
Commercial enterprise means any for-profit activity formed for the ongoing conduct of lawful business, including:
- A sole proprietorship;
- Partnership (whether limited or general);
- Holding company;
- Joint venture;
- Corporation;
- Business trust; or
- Other entity, which may be publicly or privately owned.
This definition includes a commercial enterprise consisting of a holding company and its wholly owned subsidiaries, if each such subsidiary is engaged in a for-profit activity formed for the ongoing conduct of a lawful business.
This definition does not include noncommercial activity, such as owning and operating a personal resi An EB-5 investor must invest the required amount of capital in a new commercial enterprise that will create full-time positions for at least 10 qualifying employees.
- For a new commercial enterprise not located within a regional center, the new commercial enterprise must directly create the full-time positions to be counted. This means that the new commercial enterprise (or its wholly ownedsubsidiaries) must itself be the employer of the qualifying employees.
- For a new commercial enterprise located within a regional center, the new commercial enterprise can directly or indirectly create the full-time positions.
- Direct jobs establish an employer-employee relationship between the new commercial enterprise and the persons it employs.
- Indirect jobs are held outside of the new commercial enterprise but are created as a result of the new commercial enterprise.
- In the case of a troubled business, the EB-5 investor may rely on job maintenance.
- The investor must show that the number of existing employees is, or will be, no less than the pre-investment level for a period of at least two years.
A troubled business is one that has been in existence for at least two years and has incurred a net loss during the 12- or 24-month period before the priority date on the immigrant investor’s Form I-526. The loss for this period must be at least 20% of the troubled business’ net worth before the loss. When determining whether the troubled business has been in existence for two years, USCIS will consider successors in interest to the troubled business when evaluating whether they have been in existence for the same period of time as the business they succeeded.
A qualifying employee is a U.S. citizen, lawful permanent resident, or other immigrant authorized to work in the United States, including a conditional resident, temporary resident, asylee, refugee, or a person residing in the United States under suspension of deportation. This definition does not include immigrant investors; their spouses, sons, or daughters; or any alien in any nonimmigrant status (such as an H-1B nonimmigrant) or who is not authorized to work in the United States.
Full-time employment means employment of a qualifying employee by the new commercial enterprise in a position that requires a minimum of 35 working hours per week. In the case of the regional center program, full-time employment also means employment of a qualifying employee in a position that has been created indirectly that requires a minimum of 35 working hours per week.
A job-sharing arrangement where two or more qualifying employees share a full-time position will count as full-time employment provided the hourly requirement per week is met. This definition does not include combinations of part-time positions even if, when combined, the positions meet the hourly requirement per week.
Jobs that are intermittent, temporary, seasonal, or transient do not qualify as permanent full-time jobs. However, jobs that are expected to last at least two years are generally not considered intermittent, temporary, seasonal, or transient.
Capital means cash, equipment, inventory, other tangible property, cash equivalents, and indebtedness secured by assets owned by immigrant investors, if they are personally and primarily liable and the assets of the new commercial enterprise upon which the petition is based are not used to secure any of the indebtedness. All capital will be valued at fair-market value in U.S. dollars. Assets acquired, directly or indirectly, by unlawful means (such as criminal activities) will not be considered capital for the purposes of section 203(b)(5) of the Act.
Note: Immigrant investors must establish that they are the legal owner of the capital invested. Capital can include their promise to pay (a promissory note) under certain circumstances.
The minimum investment amounts by filing date and investment location are:
| Petition Filing Date | Minimum Investment Amount – 8 CFR 204.6(f)(1). | Targeted Employment Area Investment Amount – 8 CFR 204.6(f)(2) | High-Employment Area Investment Amount – 8 CFR 204.6(f)(3) |
| Before 11/21/2019 | $1,000,000 | $500,000 | $1,000,000 |
| On or After 11/21/2019 | $1,800,000 | $900,000 | $1,800,000 |
Future adjustments will be tied to inflation (per the Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers, or CPI-U) and occur every five years.
A TEA can be, at the time of investment, either:
- A rural area; or
- An area that has experienced high unemployment (defined as at least 150% of the national average unemployment rate).
A rural area is any area other than an area within a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) (as designated by the Office of Management and Budget) or within the outer boundary of any city or town having a population of 20,000 or more according to the most recent decennial census of the United States.
A high-unemployment area may be any of the following areas, if that area is where the new commercial enterprise is principally doing business and the area has experienced an average unemployment rate of at least 150% of the national average unemployment rate:
- An MSA;
- A specific county in an MSA;
- A county in which a city or town with a population of 20,000 or more is located; or
- A city or town with a population of 20,000 or more outside of an MSA.
A high-unemployment area may also consist of the census tract or contiguous census tracts in which the new commercial enterprise is principally doing business, which may include any or all directly adjacent census tracts, if the weighted average unemployment for the specified area based on the labor force employment measure for each tract is 150% of the national unemployment average.
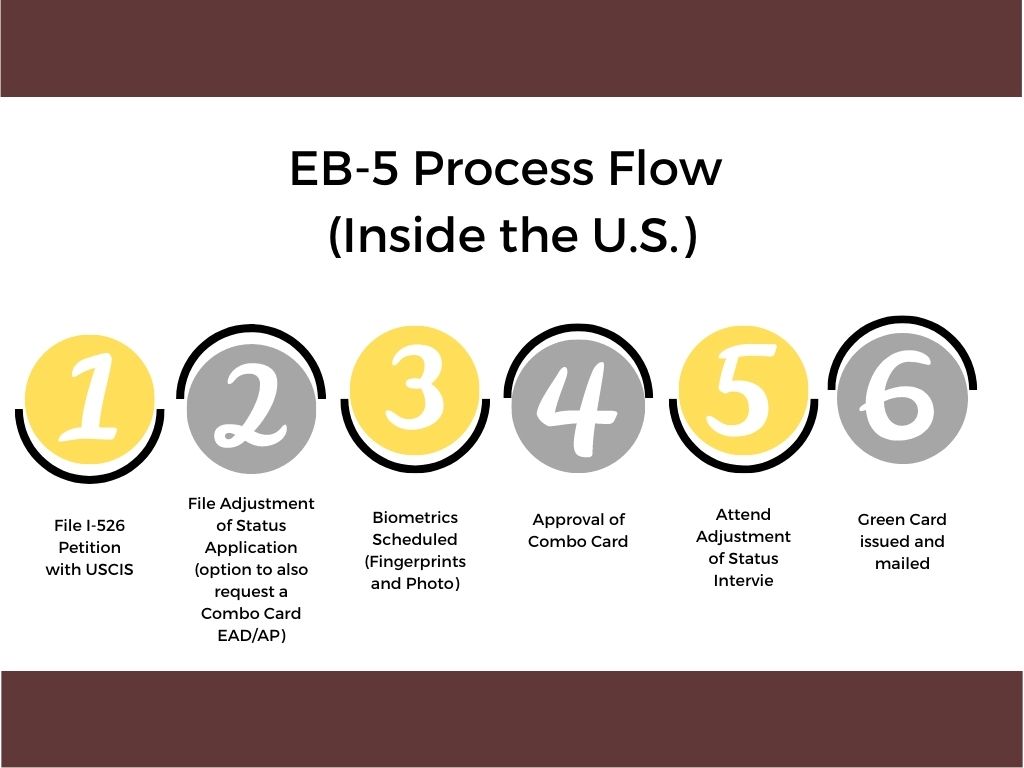
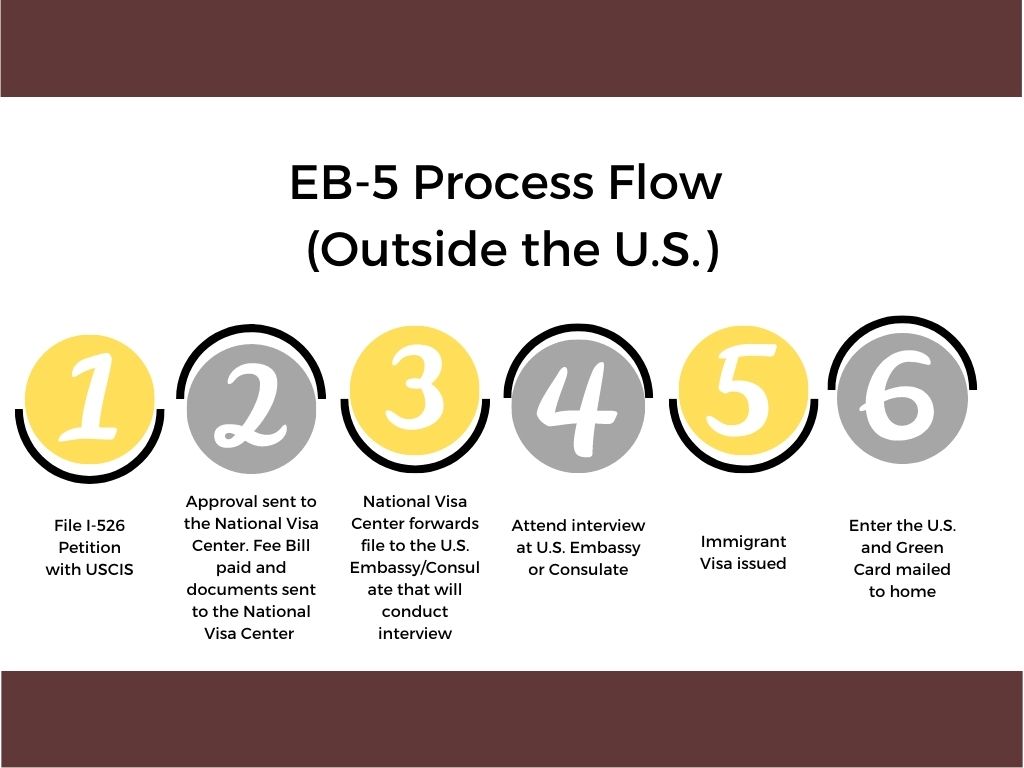
By the time the visa petition is filed, the foreign national must decide whether he/she will apply for permanent residence here in the United States or at a U.S. consulate or embassy abroad.
Application for Lawful Permanent Residence
Presuming there is no backlog for an immigrant visa for the foreign national’s country of chargeability and preference category as determined by the labor certification filing date or the filing of the visa petition (i.e., priority date), if the foreign national is in the United States on a temporary nonimmigrant visa, or if he or she otherwise qualifies by regulation, the foreign national and his or her family may be eligible to apply for adjustment of status to lawful permanent resident with the regional service center of USCIS. If the foreign national is not in the United States, or does not qualify for adjustment of status, then the foreign national and his or her family must apply for immigrant visas at the appropriate U.S. consulate in his or her home country or country of residence. If permanent residence is applied for in the United States, it is called “adjustment of status” processing. If applied for outside the United States, it is called applying for an immigrant visa.” The result of either is the same: permanent residence.
As part of the ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application process, a foreign national may also apply for an employment authorization document (EAD) and advance parole (AP). A foreign national is not required to apply for an EAD or AP at the time he/she files his/her ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application or while his/her ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application is pending. It can take U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS, legacy Immigration and Naturalization Service) several months to approve a foreign national’s ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application. If a foreign national’s circumstances change during that time period, having the approved EAD and AP available will provide maximum flexibility even if for now a foreign national plan to continue to maintain his/her nonimmigrant status (such as H-1B, L-1, or O-1 status).
What is an EAD?
A foreign national can obtain an EAD card by filing an EAD Application at the same time he/she files his/her ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application, or after the ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application is filed. Once approved, the EAD card allows its holder to work for any employer while the card is valid. By contrast, a foreign national’s nonimmigrant status (H-1B, O-1, L-1, etc.) allow him/her to work only for the employer who filed the nonimmigrant petition. Once a foreign national has an EAD in hand, he/she may legally work for any employer (but remember that even with an EAD, a foreign national must have the intent to work for the sponsoring employer, in case of employment-based permanent residence, at the time his/her ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application is approved). EADs are valid for up to one year at a time. Spouses and dependent children may also obtain EADs, if desired.
What is an Advance Parole?
A foreign national can obtain AP by filing an AP Application at the same time he/she files his/her ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application, or after the ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application is filed. Once approved, AP allows a foreign national to leave the United States and re-enter without having a valid nonimmigrant visa stamp in his/her passport. Unless a foreign national is maintaining H-1B or L-1 status, after his/her ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application is filed, a foreign national must obtain AP before leaving the United States. For example, if a foreign national has O-1 status and he/she files an ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application and then later a he/she leaves the United States without AP, his/her ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application will be considered by USCIS to have been “abandoned” and will be denied. This would cause great delay and expense because it could take weeks or months to get a foreign national back to the United States in new O-1 status, and then a new ADJUSTMENT OF STATUS Application package would have to be filed all over again. Traveling with AP prevents such problems from occurring. AP is valid for multiple entries during the validity of the document.
At the lawful permanent residence application stage, the USCIS (or consular office) will ask whether the foreign national has: (1) been a member of the Communist Party, terrorist groups, or similar organizations; (2) been arrested or convicted of any crimes; (3) ever received public assistance, (4) lied to obtain a visa, (5) worked in the United States without permission, or (6) overstayed his/her legal status, etc. We will go into more detail about these factors later.
In general, employment-based and family-based adjustment of status cases are subject to interviews with the local USCIS district office. Individuals who undergo consular processing of employment-based or family-based cases are also required to attend an interview.
At the end of this step, the foreign national will be granted permanent residence and issued a “green card.”